Search Lab Grown Diamonds
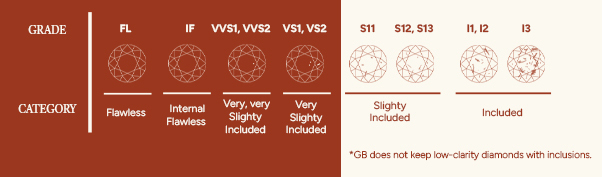
A diamond’s clarity refers to the presence of impurities on and within the stone. Even when grown in a lab, tiny imperfections might be visible. These are called flaws or inclusions. They form during the growing process and are unique to each stone. The term "eye clean" refers to diamonds whose inclusions generally cannot be seen without magnification, and are typically graded SI or higher on the clarity scale.
A grading report or diamond certificate is an independent, expert opinion on the quality of the diamond. Gemologists from the world's leading grading labs use special equipment to measure the weight and dimensions of the diamond and assess quality characteristics such as cut, color, and clarity. Grown Brilliance only utilizes the most distinguished grading labs.Please contact us to request the grading report.
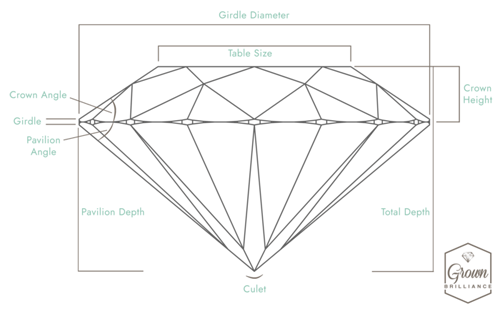
The length-to-width ratio compares the length of a diamond to its width to show how elongated a fancy-shaped diamond appears when viewed from the top. Length-to-width ratio is a matter of personal preference with some individuals preferring a more elongated shape and others a more equal or square shape. It is calculated as length divided by width.
Fluorescence refers to a diamond's tendency to emit a soft colored glow when subjected to ultraviolet light (such as a "black light"). Overall, diamond fluorescence should not be a major factor in the purchase of a diamond since its effects are negligible. Fluorescence grades include Very Strong, Strong, Medium, Faint, None.
| Diamonds Available: 0 |
|---|
| Quick Ship | Shape | Carat | Color | Clarity | Cut | CERT. | Polish | Symmetry | DEPTH | Price | Compare | Wishlist | Choose |
|---|
Select your perfect diamond from thousands of ethically created diamonds, then choose a setting and we will show you your custom-made ring.
Discover the perfect lab grown diamond with Grown Brilliance. Our extensive collection offers a range of shapes, sizes and styles to suit every preference. Each diamond is ethically sourced and crafted with precision, ensuring exceptional quality. Use our intuitive search filters to explore, compare and find a diamond that resonates with your personal style and values.
How to Find Your Lab Grown Diamond?
Searching for the perfect loose lab grown diamond at Grown Brilliance is easy with our straightforward user-friendly search tool.
-
Choose your diamond shape. At Grown Brilliance, we offer a huge range of popular and fancy diamond shapes, from classic round and princess cuts to vintage asscher and marquise.
-
Select your carat weight. Our loose diamonds are available in carat weights ranging from 0.90 to over 20.00. For delicate jewelry or side stones, choose smaller carat weights so you don't overwhelm the design. If you want to make a statement or love the striking look of a solitaire engagement ring, opt for a larger carat weight.
-
Find your color. Diamond color is graded on a scale from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow or brown). The highest quality diamonds are colorless, which includes D, E, and F color grades, while those closer to Z have a noticeable hue, affecting their brilliance and value. Our loose lab grown diamonds are only available in colors from D to H, ensuring you get the most brilliant gemstones possible.
-
Choose your cut. Diamond cut refers to how well a diamond has been shaped and faceted. Diamonds are graded on a scale consisting of six levels, from Ideal to Poor, assessing the stone's proportions, symmetry and polish. We pride ourselves on offering diamonds that reflect the top quality of lab created diamonds, so we only offer diamonds in Ideal, Excellent, and Very Good qualities.
-
Select the diamond's clarity. Diamond clarity measures the presence of internal inclusions and external blemishes. It's graded from Flawless (no imperfections) to Included (visible inclusions). Our loose lab grown diamonds are available in Flawless (FL) to Very Slightly Included level 2 (VS2), so you can choose a diamond clarity that matches your budget.
-
Determine Your Budget. Use our sliding tool to select your minimum and maximum budget range. The lowest prices start around $500 and reach up to $100,000 or more.
Once you have applied all the filters, we'll provide you with a list of all the diamonds we currently have in stock that meet your requirements. Click on the Details option to view your selected diamond and use the 360° viewing tool to examine your gem from every angle.
Or, compare several of our diamonds side-by-side by selecting the check box and add your favorite diamonds to your wishlist while you browse the rest of our site.
If you want even more details about the 4Cs of diamonds, click here.
Take the Quiz
If you can't decide on a diamond, take our easy quiz. Simply click on the link and you'll be asked which of our popular cuts appeal to you most, including round, oval, cushion and pear.
Then, select a price range to match your budget. Finally, decide which quality level matters to you most. Choose from Good, which suggests you prefer the largest carat diamond for your budget; Better, which shows that you want the right balance of diamond quality at the best price; and Best, which means we'll filter your options according to the 4C's to give you the highest quality diamond possible.
Why Choose Grown Brilliance Diamonds?
Ethical sourcing is at the heart of what we do. We believe in obtaining our diamonds responsibly and ensuring every step of the process meets our high ethical standards. You can be certain they are never involved in conflict, violence, or war, and they meet all local safety protocols and labor laws. To learn more about conflict-free diamonds, click here. Our recyclable packaging also reflects our journey towards sustainability
We understand that buying lab grown diamonds is about more than just the price, but we also know that fair pricing matters. That's why we stand behind GB365, which is our commitment to offer our diamonds to you at our best price every day, without ever going on sale. We make your experience as smooth and worry-free as possible, offering free shipping, a lifetime warranty and free returns.
Lab created diamonds are real diamonds. Lab grown diamonds are chemically, physically and optically identical to natural diamonds. The key difference lies in their origin – while natural diamonds are formed in the Earth’s mantle over billions of years, lab created diamonds are grown in controlled environments using advanced technological processes. This makes them a more ethical choice without compromising quality or brilliance.
Yes. Lab grown diamonds are simple to appraise and insure. Depending on the policy, this may protect them against loss, theft or damage. Your Grown Brilliance receipt or invoice will typically suffice in order to obtain insurance for your lab grown diamond jewelry from your insurer.
Similar to mined diamonds, lab created diamonds value is determined by many factors, including the costs to produce them, market demand, and the quality of the diamond. Most diamonds, both mined and lab created, have a resale value and sell for a portion of the original sale price. You can receive a higher value based on several factors, such as if the diamond is in good condition and has excellent quality. Keep your diamond’s certification, if you were issued one, because it may be helpful if you decide to sell.